Food poisoning

Fish can carry a wide variety of bacteria, viruses and parasites that can cause a host of nasty illnesses. For example, tilapia, one of the most commonly farmed fish, tends to carry the bacterium Plesiomonas shigelloides which causes diarrhoea, nausea, vomiting and fever (Cortés-Sánchez et al., 2021). There are many other types of food poisoning that eating fish can cause and thorough cooking doesn’t always prevent it because the raw fish can contaminate kitchen surfaces.
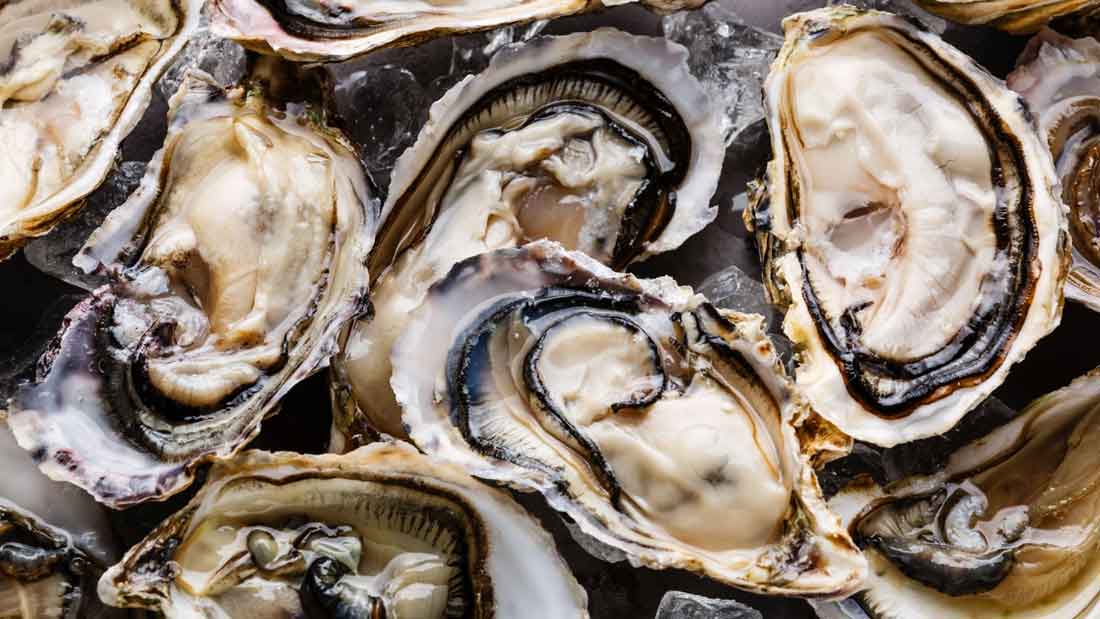
The NHS warn that pregnant women, babies and children should avoid eating raw shellfish (such as mussels, clams and oysters) because of the high risk of food poisoning (NHS, 2018). They may carry norovirus – the vomiting bug that can cause severe sickness and fever. Both raw and cooked shellfish can also contain some toxins that may cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, headaches, numbness, breathing difficulties, memory loss, disorientation and abdominal pain.
Going fish-free is not just a healthy choice, it’s also an ethical and sustainable one. If you’re used to meals based around fish and other animal products, the idea of a plant-based diet may be daunting but we’re here to help make it super easy!
Sign up to our daily emails for a week to receive mouth-watering meal plans, nutritional advice and health information.
If you want to try it for a month, sign up to 30 days of delicious vegan recipes, tips and product info… all free!
All about fish
Find all the above and more in Viva!’s resources on fish:
Delve deep into the science beyond health claims and fish in The Fish Report.
Find out more about fish, fish oil and omega-3s in the Fish-free for Life guide.
Or see the summary in this handy Fishing for Facts factsheet.