Definition of Veganism

Vegans don’t eat, wear or use anything from animals — whether from land animals (meat, dairy, eggs, honey, shellac, leather, fur etc) or from water animals (fish, prawns, crab, lobster etc). Vegans also exclude, as far as is practicable, all forms of animal exploitation and cruelty
Other definitions explained

Vegans don’t eat anything that comes from an animal. That includes meat, milk, cheese, other dairy products, fish, eggs, honey and some more obscure animal products such as shellac and beeswax. This means no damaging animal protein, animal fats or cholesterol in their diet.
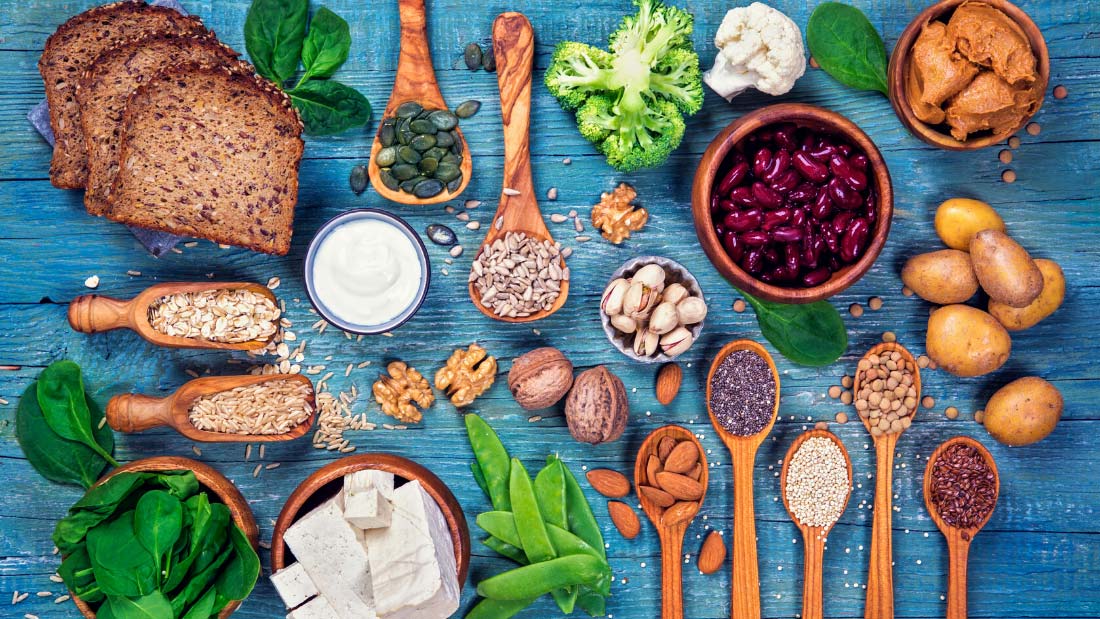
Vegans tend to have a healthier diet packed with good stuff! Vegans eat bread, pasta, rice, fruit and vegetables, nuts, beans, peas, lentils and other pulses. We can also eat meat, fish and dairy alternatives often made from soya, almonds, coconuts, oats and nuts. Pretty much anything can be made vegan!
Have a look at what vegans eat at our Vegan Recipe Club – there are hundreds of delicious recipes just waiting for you to try.
Why is it healthy?
The cornerstones of a healthy diet are fruit and vegetables, wholegrains (brown rice, wholemeal bread, oats etc), pulses (peas, beans, lentils), nuts and seeds. And these are the basics of a healthy vegan diet.
A varied vegan diet contains no cholesterol, plenty of fibre, healthy carbs, ‘good’ fats and protein, a wide range of health-protecting antioxidants and essential nutrients. This super-nutrient package helps to:
- lower your blood pressure and unhealthy cholesterol – and can return it to normal
- lower your risk of heart disease – and can even reverse it
- lower your risk of type 2 diabetes – or help you treat it and get off meds
- lower your risk of cancer – vegans have up to 20 per cent lower risk
- make it easier to achieve a healthy weight – whilst eating plenty of food!
Find out more about Going Vegan.

Veganism is a celebration of life! It’s not just a diet, it’s a way of living and a protected belief system. Veganism doesn’t simply mean avoiding certain foods. It affects the clothes you wear, the cosmetics you use, the products you buy, and the way you see and interact with the world.


Animals
Veganism is a celebration of life! It’s not just a diet, it’s a way of living and a protected belief system. Veganism doesn’t simply mean avoiding certain foods. It affects the clothes you wear, the cosmetics you use, the products you buy, and the way you see and interact with the world.
- Check out: Viva! Animals

Health
Vegans have a significantly reduced risk of heart disease, diabetes, dementia and some cancers, with lowered cholesterol and increased energy levels. A balanced, wholefood vegan diet is packed with a wide range of healthy, disease busting foods high in vegetable protein, fibre, complex carbohydrates, antioxidants, vitamins, minerals and good fats. Being vegan also means no damaging animal protein, animal fats, cholesterol, animal hormones or pus – plus a much reduced chance of food poisoning.
- Check out: Viva! Health

Planet
Concern for the environmental devastation caused by animal agriculture and fishing are also key reasons why vegans avoid animal products. The decimation of wildlife and natural habitats is one of the greatest challenges the world faces. As food production expands to meet the world’s appetite for meat, eggs, dairy and fish, emissions from animal agriculture continue to rise. The only way to stop this is to change the way we eat.
- Check out: Viva! Planet

Here are some of the most frequently asked questions about veganism. If you don’t see your question here, we have an entire page dedicated to vegan FAQs, plus our vegan health FAQs.
How many vegans are there?
It is hard to estimate how many vegans there are. According to the Waitrose Food & Drink Report 2018 – 19;
- Thirty-three per cent of the population are cutting down on – or cutting out – meat
- 9.5% are vegetarian 3% are vegan – which equates to 2 million people calling themselves vegan
- 60% of vegans and 40% of vegetarians have adopted the lifestyle over the past five years.

One thing is for certain — veganism is rapidly growing and is gaining momentum every day.
Are vegans healthier?
Yes, a vegan diet provides all the nutrients and minerals you need, without the added animal fat, animal protein and growth factors which come from meat and dairy. So vegans do tend to be healthier. See our vegan health FAQs for more.
Where do vegans get protein?
It is a misconception that a vegan diet is low in protein. Most people in Western societies have the opposite problem – far too much protein – and protein deficiency is almost unheard of. The best plant sources of protein include pulses (lentils, beans, chickpeas, peas and soya), nuts, seeds and wholegrains (wholemeal bread, wholewheat pasta and brown rice). One large serving of cooked tofu could provide up to half the protein you need in one day!
Read more about protein on our A-Z of nutrients.
Where do vegans get calcium?
A healthy vegan diet containing the foods listed below on a daily basis will cover your calcium needs. The best plant sources of calcium are: tofu, fortified vegan breakfast cereal, plant-based milk alternatives fortified with calcium, dried figs, kale, sesame seeds and tahini, tempeh, wholemeal bread, baked beans, butternut squash, almonds and Brazil nuts, spring greens and watercress.
Read more about calcium.

“The most powerful action you can take to end animal suffering, protect the environment and reduce disease is to go vegan. Society is changing. People are increasingly accepting the benefits of veganism; the tide is turning. Support Viva! and help us campaign for a better world.”
— Juliet Gellatley, Viva! founder and director.